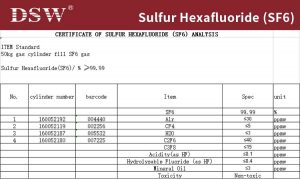
SF6 Gas, Sulfur Hexafluoride

sulphur hexafluoride
is an anthropogenically produced compound, mainly used as a gaseous dielectric in gas insulated switchgear power installations.

Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a synthetic fluorinated compound with an extremely stable molecular structure. Because of its unique dielectric properties, electric utilities rely heavily on SF6 in electric power systems for voltage electrical insulation, current interruption, and arc quenching in the transmission and distribution of electricity. Yet, it is also the most potent greenhouse gas known to-date. Over a 100-year period, SF6 is 22,800 times more effective at trapping infrared radiation than an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide (CO2). SF6 is also a very stable chemical, with an atmospheric lifetime of 3,200 years. As the gas is emitted, it accumulates in the atmosphere in an essentially un-degraded state for many centuries. Thus, a relatively small amount of SF6 can have a significant impact on global climate change.
sulphur hexafluoride gas molecules are combined by one sulfur and six fluorine atoms. This gas was first realized in the year of 1900 in the laboratories of the Faculte de Pharmacie de, in Paris. In the year of 1937, General Electrical Company first realized that SF6 gas i.e. sulfur hexafluoride gas can be used as insulating material.
sulphur hexafluoride is used in medical applications
One of the most important uses of SF6 is in the medical industry, where it is used as a contrast agent for MRI scans. When SF6 is injected into the bloodstream, it enhances the image quality of the MRI and makes it easier for doctors to detect and diagnose medical conditions.
SF6 is also used in the treatment of retinal detachment, a condition that can lead to blindness. In this application, SF6 is injected into the eye to help reattach the retina and prevent further damage.
Overall, SF6 has proven to be a valuable tool in the medical industry, helping doctors to diagnose and treat a range of medical conditions.