WELDING GAS MIXTURES
DSW™ argon (Ar) and carbon dioxide (CO2) blends are versatile mixtures for welding carbon, low-alloy and some stainless steels. By increasing the CO2 content, you can increase weld penetration and bead wetting characteristics however, increased splattering may also occur. Ar and CO2 blends can be used to join a wide range of material thicknesses using a variety of metal transfer modes.
We also offer a series of WELDING GAS MIXTURES Ar and oxygen (O2) blends that are commonly used for conventional and pulsed spray transfer on clean (little to no scale or residual oil), plain carbon and stainless steel. These blends offer 1, 2 or 5% oxygen and provide good arc stability and low levels of spatter and fume. Higher levels of oxygen will also increase puddle fluidity that may make out-of-position welding more difficult.
We want you to get the most out of your industrial gas. Take a look at the blends below and contact us to find the one that’s right for your application.
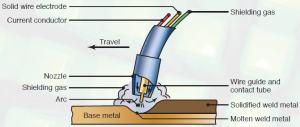
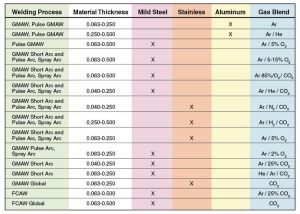
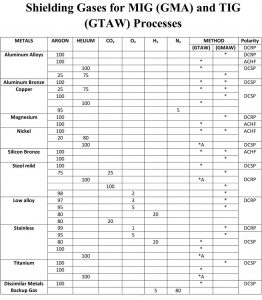
Charistics of MIG Welding Gasses
Different gasses produce different types of weld penetration and arc characteristics. Here are the basics:
Argon gas has shallow wide penetration and has a very smooth fluid like arc.
Helium produces a very hot weld with good weld productivity and mild penetration with a fluid arc.
Carbon Dioxide produces a deep narrow penetration with a stiff harsh arc that works well in out of position welding.
Adding Carbon Dioxide to Argon or Helium deepens penetration and stiffens the arc improving out of position welding.
Oxygen added to Helium or Argon in small amounts deepens the weld penetration and stiffens the arc characteristics.
Adding Helium to any mix makes the arc hotter.