The Ultimate Guide to Cryogenic Liquid Storage Vessels: Everything You Need to Know
As industries across the world continue to grow and expand, the need for safe, reliable, and efficient storage solutions becomes increasingly important. For industries dealing with cryogenic liquids, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, the stakes are even higher. Cryogenic liquids must be stored at extremely low temperatures to remain in their liquid state, and any failure in the storage system can lead to catastrophic consequences. That’s why it’s crucial for industries dealing with cryogenic liquids to understand the importance of proper storage vessels and their maintenance. In this ultimate guide to cryogenic liquids storage vessels, we’ll explore everything you need to know about these essential tools, from their design and construction to their operation and maintenance. Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights you need to ensure safe and reliable storage of cryogenic liquids.
Types of Cryogenic Liquids and Their Applications
Cryogenic liquids are used in a variety of industries for different purposes. The four most common cryogenic liquids are liquefied natural gas (LNG), nitrogen, oxygen, and argon. LNG is used as a fuel for transportation, heating, and power generation. Nitrogen is used in the food and beverage industry to preserve food and create an inert atmosphere. Oxygen is used in the medical industry to treat respiratory problems, and argon is used in the welding industry to create an inert atmosphere.
Each cryogenic liquid has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications. For example, LNG has a high energy density, making it an excellent fuel for transportation. Nitrogen has a low boiling point, making it ideal for use in cryopreservation. Oxygen is highly reactive, making it useful in combustion and oxidation processes. Argon is an inert gas that helps prevent oxidation during welding.
cryogenic liquid storage tank is to fill and store cryogenic liquid. For the safe use of cryogenic liquid storage tanks, comprehensive consideration should be given to the dangerous properties of gas, cryogenic protection effects, surrounding environmental conditions, and characteristics of pressure vessels, etc., and appropriate technical management measures should be taken to ensure safe operation.
Cryogenic Liquid Storage Vessel Design
Cryogenic liquid storage vessels are designed to store cryogenic liquids at extremely low temperatures. They are typically made of high-quality materials that can withstand the extreme cold and pressure of cryogenic liquids. The design of cryogenic liquid storage vessels is critical to ensuring the safe and reliable storage of these liquids.
Cryogenic liquid storage vessels come in different shapes and sizes, depending on their intended use. They can be vertical or horizontal and can range in size from small portable containers to large stationary tanks. The design of cryogenic liquid storage vessels is also dependent on the type of cryogenic liquid being stored and its intended use.
The design of cryogenic liquid storage vessels includes features such as double-walled construction, vacuum insulation, and pressure relief systems. Double-walled construction provides an additional layer of protection against leaks and spills. Vacuum insulation helps to maintain the low temperature of the cryogenic liquid and reduces heat transfer. Pressure relief systems are designed to prevent overpressure in the storage vessel, which can lead to explosions.
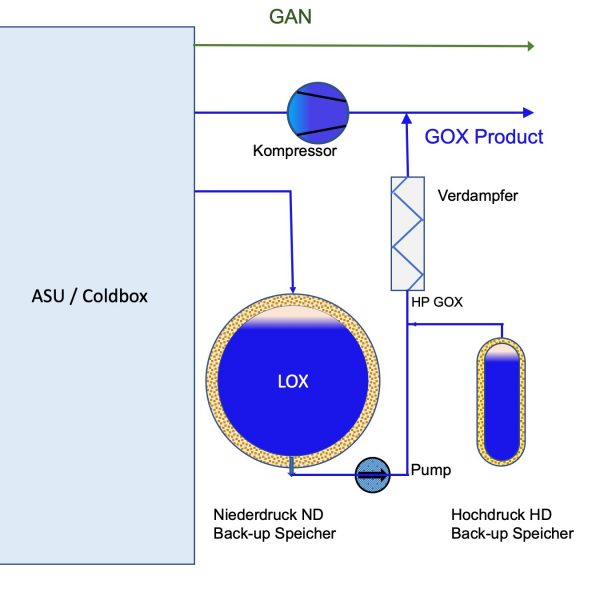
Industrial gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, argon and hydrogen are being produced in gaseous form or as cryogenic liquids. For storage or back-up cryogenic liquid tanks are used.
Example: Back-up systems
Main Components:
Tank liquid storage
Pump raises liquid pressure
Vaporiser liquid vaporised to ambient temperature

The structure and type of cryogenic liquid storage tanks.
In recent years, the low-temperature liquid market has become increasingly popular. The sales of liquid oxygen, liquid argon, liquid nitrogen, and liquid carbon dioxide, and LNG and natural gas have increased sharply. Non-steel products are an important part of revenue. The production, storage, and transportation of cryogenic liquids cannot be separated from cryogenic storage tanks.
Cryogenic Vacuum Standard Tanks
VIT (Vacuum Isolated Tank)
Vacuum Insulated Tank- typically for pressures up to 5 bar (g)
storage of liquid to be delivered to pump or tanker
VIE (Vacuum Isolated Evaporator)
typically for pressures up to 35 bar (g)
designed to operate with a vapouriser to supply gas to customer
suitable for supply of large quantities of product for a short time
inner vessel stainless steel, outer vessel carbon steel
insulation: vacuum interspace, perlite filled
vessels often supplied with instrumentation eg level indication, pressure protection

During the normal use of the cryogenic liquid storage tank, a special person should be responsible for the roving inspection. Check that the pressure of the inner container does not exceed the working pressure of the storage tank. If the pressure is exceeded, pressure relief measures should be taken. Check the status of each valve and the leakage status, and find that the status is different or there is a leak.
Cryogenic Liquid Storage Vessels Design
Flat Bottom Tanks
atmospheric storage, held a few millibar above atmospheric pressure
large quantities single product
inner vessel stainless steel, outer vessel carbon steel
site built tank
emergency flap valves main in/outlets
insulation: perlite interspace with nitrogen purge
Regularly check the vacuum in the jacket of the cryogenic liquid storage tank. If the vacuum deteriorates, take additional vacuuming measures (storage of the tank should be invited to the professional unit or the original manufacturing unit). If you find that there are various failures of the cryogenic liquid storage tank equipment and accessories, you should always find out the reason, make correct analysis and judgment, and take reasonable solutions to ensure its continuous normal operation and safe use.
Safety Considerations for Cryogenic Liquid Storage Vessels
Cryogenic liquid storage vessels can be extremely dangerous if not handled properly. They are highly volatile and can ignite under certain conditions. They are also extremely cold and can cause severe frostbite or hypothermia if they come into contact with skin. Additionally, they are highly compressible and can cause explosions if not handled properly.
To ensure the safe and reliable storage of cryogenic liquids, it’s essential to follow proper safety procedures. This includes proper training for all personnel who will be handling cryogenic liquid storage vessels, regular inspections and maintenance of storage vessels, and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment. It’s also critical to ensure that all storage vessels are designed and constructed to meet industry standards and regulations.
Choosing the Right Cryogenic Liquid Storage Vessel
Choosing the right cryogenic liquid storage vessel is critical to ensuring safe and reliable storage of cryogenic liquids. The choice of storage vessel is dependent on the type of cryogenic liquid being stored, its intended use, and the environmental conditions in which it will be used.
When choosing a cryogenic liquid storage vessel, it’s essential to consider factors such as the size and shape of the vessel, the insulation material used, the safety features included, and the material used in its construction. It’s also important to ensure that the storage vessel meets industry standards and regulations.
what is Cryogenic liquid storage vessels?
Cryogenic liquid storage vessels, also referred to as dewars, are the most common way to store large quantities of hydrogen. Super-insulated low pressure vessels are needed to store liquid hydrogen at -253°C (-423°F). The pressure of liquid hydrogen is no more than 5 bar (73 psig).










No comment