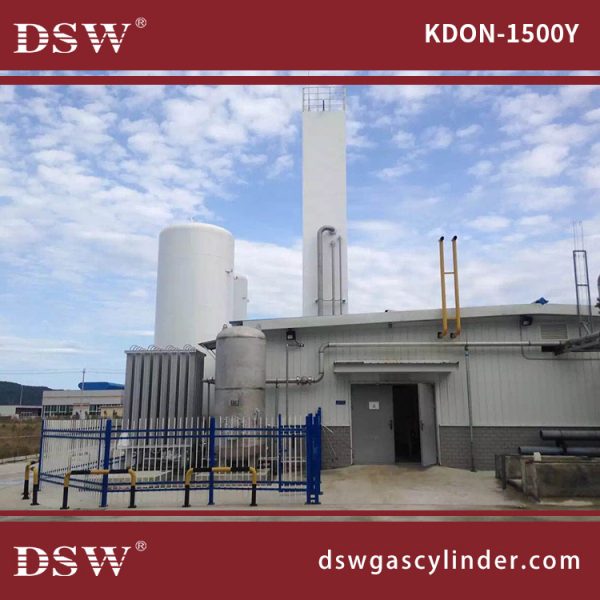
Air Separation Unit for Oxygen, Nitrogen
Air separation units (ASUs) are key utility purveyors to several major industries, including electronics, metallurgy, petroleum refining, and chemical processing.
Bulk production of atmospheric gases follows the cryogenic separation route, which is energy-intensive owing to the need to compress large volumes of air.
We engineer & manufacture all critical components in-house to ensure reliable operations and low lifecycle costs.
Our vast portfolio is designed to perfectly fit all volume, purity, product, and performance needs.
Air separation is the most common process used to extract one or all of the main constituents of atmospheric air.
The three main components are Nitrogen (78.1%), Oxygen (20.9%), and Argon (.9%). The remaining gases in the air are in trace amounts and typically not recovered.
In massive air separation units (ASU), Neon, Xenon, and Krypton are recovered in small quantities.
1、Design Condition
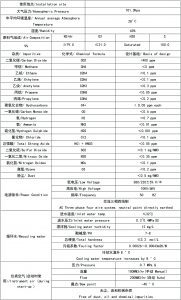
2、Main Technical Data
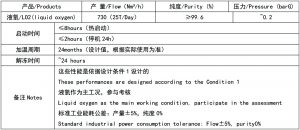
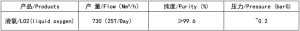
3. Performance Guarantee
3.1 Base conditions
The performance guarantee value of the plant specified in this project shall have the condition of a linkage test after the installation and acceptance of the device.
after the confirmation by clients, continuous performance assessment at full load (including mechanical performance assessment) shall be conducted, and the assessment results shall be taken as the basis for equipment acceptance
3.2 Performance Guaranteed Value
Under the design condition 1, the equipment can meet the following output:




Manufacturing Process of Air Separation Unit
There are five basic processes for producing oxygen and nitrogen: compression, purification, cooling, separation, and cylinder filling.
Basic Air Separation Unit Components
Air Compression :
We use the latest and air-cooled air compressors to compress the atmospheric air. The equipment has a suction filter to suck the atmospheric air and leave behind the impurities mixed with it.
Air Purification:
Even after using high-quality air compressors with attached suction filters, a few impurities, such as carbon dioxide, dust, etc., get inside the air. Such contaminants are alleviated in this second stage by using a process skid.
Air Cooling:
The purified air must be cooled to -165 to -170 degrees centigrade to make the air liquid. This is because liquid air gets separated easily. For this purpose, we have high-end and advanced expenders.
Air separation: Once the air becomes liquid, the air separation units separate the air into oxygen and nitrogen. We use stainless steel units as they do not react with oxygen and thus guarantee pure outputs.
Cylinder filling by Liquid Oxygen Pumps: This is the last step, where we have liquid oxygen pumps to fill in cylinders at the required pressure. With liquid oxygen pumps, there is no gas loss while cylinders fill in.