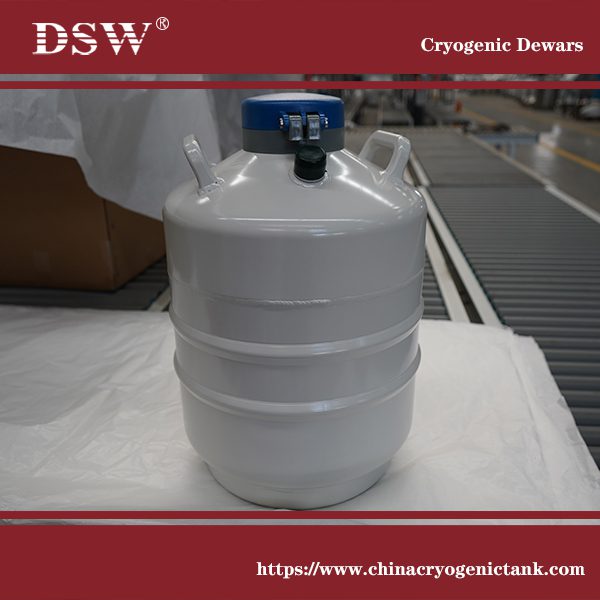
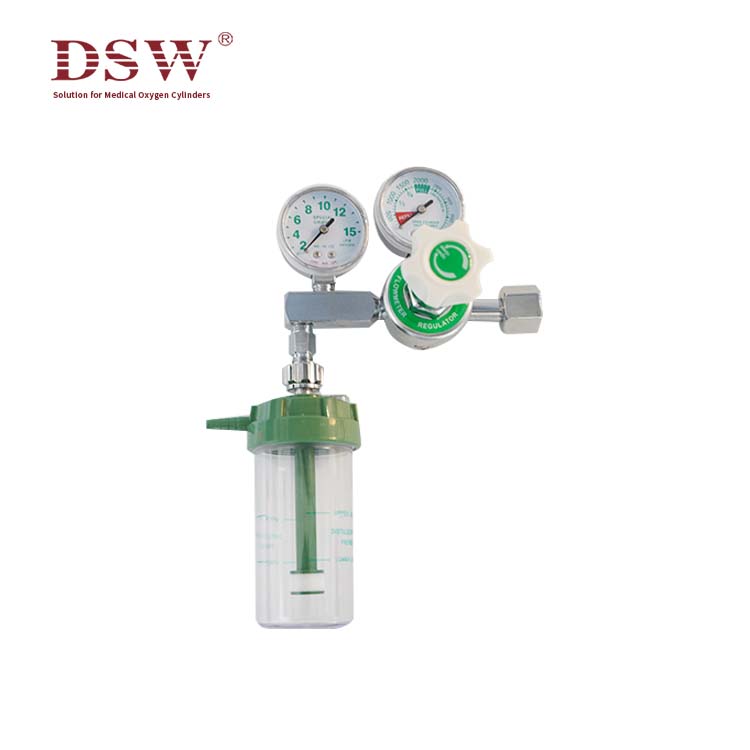
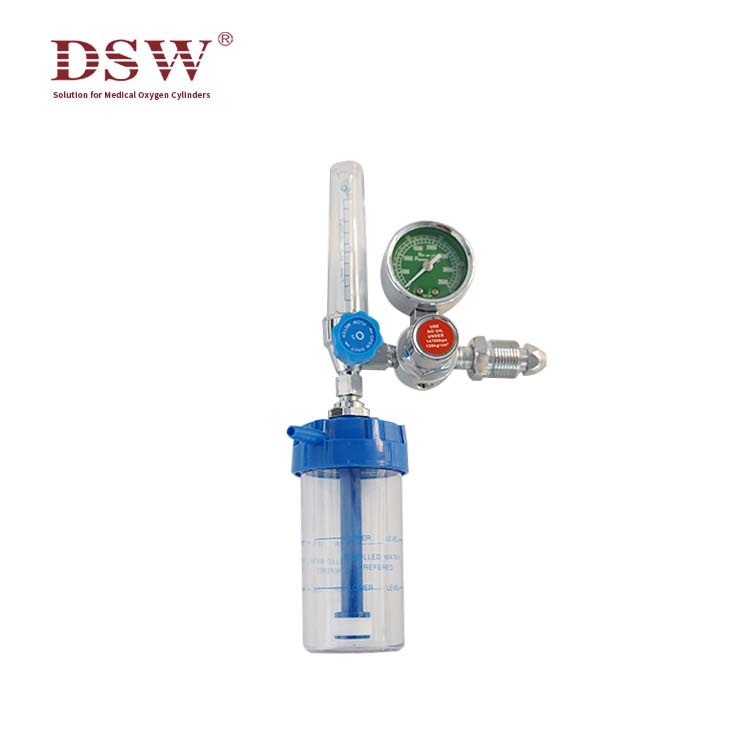
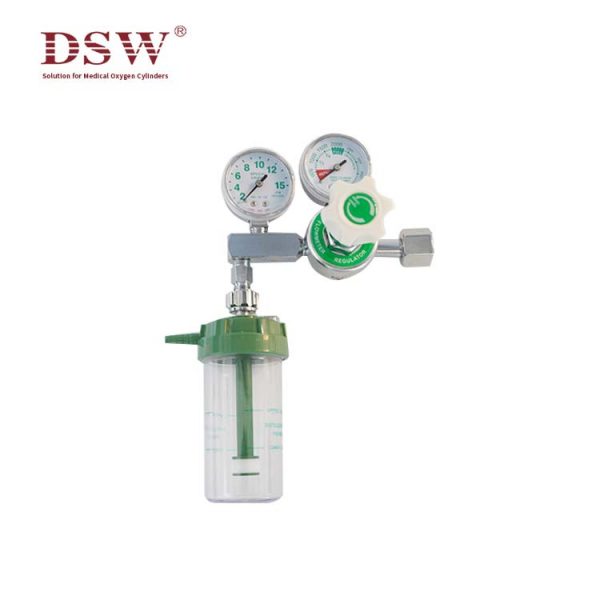
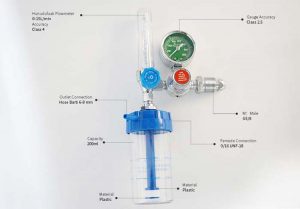
Compressed Gas Regulator- Supplied by DSW
A standard compressed gas pressure regulator incorporates a gas-loaded or spring-loaded diaphragm mechanism that regulates the opening and closing of a gas discharge orifice.
This mechanism can be calibrated manually to provide constant delivery pressure at any value within a designated range.

How a Pressure Regulator Works
Pressure regulators are self-contained mechanical control devices that don’t rely on external power sources for operation, using sensors, valves, and controller units as components of this self-sufficient device. While both regulators and control valves appear similar, it’s essential to distinguish between them; regulators tend to be less expensive and easier to install/maintain than control valve systems; however, applications requiring larger valve sizes may benefit more from control valve systems.
Gas Pressure Regulator Types
The majority of pressure regulators are either two-stage or single-stage devices. Single-stage regulators are prone to minor variations in pressure delivery when the gas cylinder’s pressure falls. This pressure also tends to decrease with increased flow. Two-stage regulators, on the other hand, offer more constant pressure levels in different operating conditions. They do this by reducing both cylinder and delivery pressure simultaneously. This limits fluctuations in pressure during operation while minimizing their lockup potential (when the pressure above the delivery point causes the flow to cease). Lockup is more familiar with single-stage regulators than with two-stage equivalents.

The medical oxygen regulator
is a medical device for oxygen or medical air inhalation of first-aid and hypoxic patients in the hospital, including an oxygen flowmeter and a medical air flowmeter. It mainly consists of a gas pressure gauge, pressure reducer, safety valve, flow tube, flow control valve, humidification bottle, and other components.